SVG pop-op
The clinical summary below aims to offer practical advice for healthcare professionals when prescribing SGLT2i therapies for the treatment of T2DM. Please refer to the relevant individual SmPC before prescribing any SGLT2i therapy: Canagliflozin | Dapagliflozin | Empagliflozin | Ertugliflozin
The clinical summary below aims to offer practical advice for healthcare professionals when prescribing SGLT2i therapies for the treatment of T2DM. Please refer to the relevant individual SmPC before prescribing any SGLT2i therapy: Canagliflozin | Dapagliflozin | Empagliflozin | Ertugliflozin
The clinical summary below aims to offer practical advice for healthcare professionals when prescribing SGLT2i therapies for the treatment of T2DM. Please refer to the relevant individual SmPC before prescribing any SGLT2i therapy: Canagliflozin | Dapagliflozin | Empagliflozin | Ertugliflozin
The clinical summary below aims to offer practical advice for healthcare professionals when prescribing SGLT2i therapies for the treatment of T2DM. Please refer to the relevant individual SmPC before prescribing any SGLT2i therapy: Canagliflozin | Dapagliflozin | Empagliflozin | Ertugliflozin
The clinical summary below aims to offer practical advice for healthcare professionals when prescribing SGLT2i therapies for the treatment of T2DM. Please refer to the relevant individual SmPC before prescribing any SGLT2i therapy: Canagliflozin | Dapagliflozin | Empagliflozin | Ertugliflozin
The clinical summary below aims to offer practical advice for healthcare professionals when prescribing SGLT2i therapies for the treatment of T2DM. Please refer to the relevant individual SmPC before prescribing any SGLT2i therapy: Canagliflozin | Dapagliflozin | Empagliflozin | Ertugliflozin
The clinical summary below aims to offer practical advice for healthcare professionals when prescribing SGLT2i therapies for the treatment of T2DM. Please refer to the relevant individual SmPC before prescribing any SGLT2i therapy: Canagliflozin | Dapagliflozin | Empagliflozin | Ertugliflozin
The clinical summary below aims to offer practical advice for healthcare professionals when prescribing SGLT2i therapies for the treatment of T2DM. Please refer to the relevant individual SmPC before prescribing any SGLT2i therapy: Canagliflozin | Dapagliflozin | Empagliflozin | Ertugliflozin
The clinical summary below aims to offer practical advice for healthcare professionals when prescribing SGLT2i therapies for the treatment of T2DM. Please refer to the relevant individual SmPC before prescribing any SGLT2i therapy: Canagliflozin | Dapagliflozin | Empagliflozin | Ertugliflozin
The clinical summary below aims to offer practical advice for healthcare professionals when prescribing SGLT2i therapies for the treatment of T2DM. Please refer to the relevant individual SmPC before prescribing any SGLT2i therapy: Canagliflozin | Dapagliflozin | Empagliflozin | Ertugliflozin
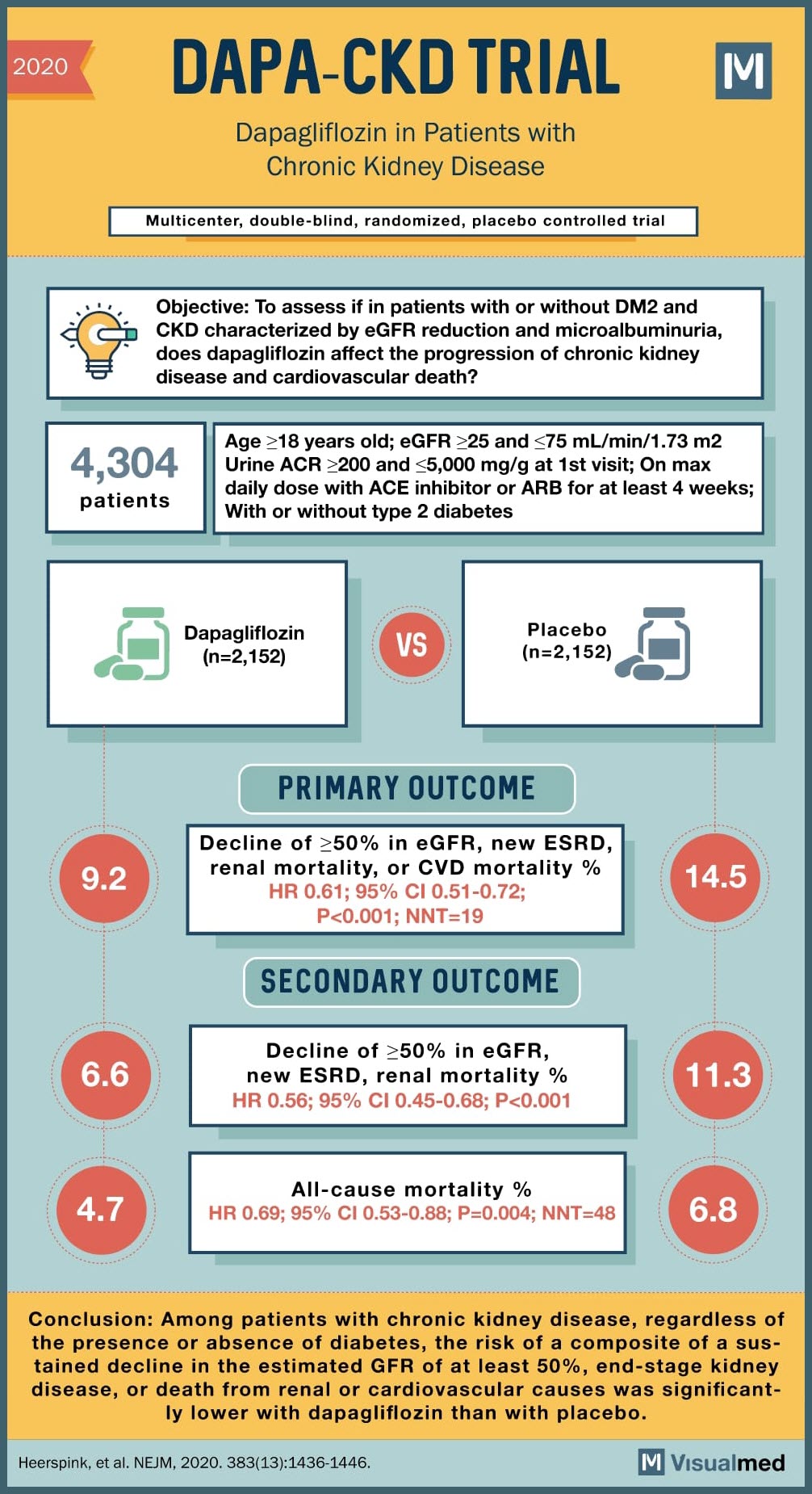
SOURCE: @Visualmedapp
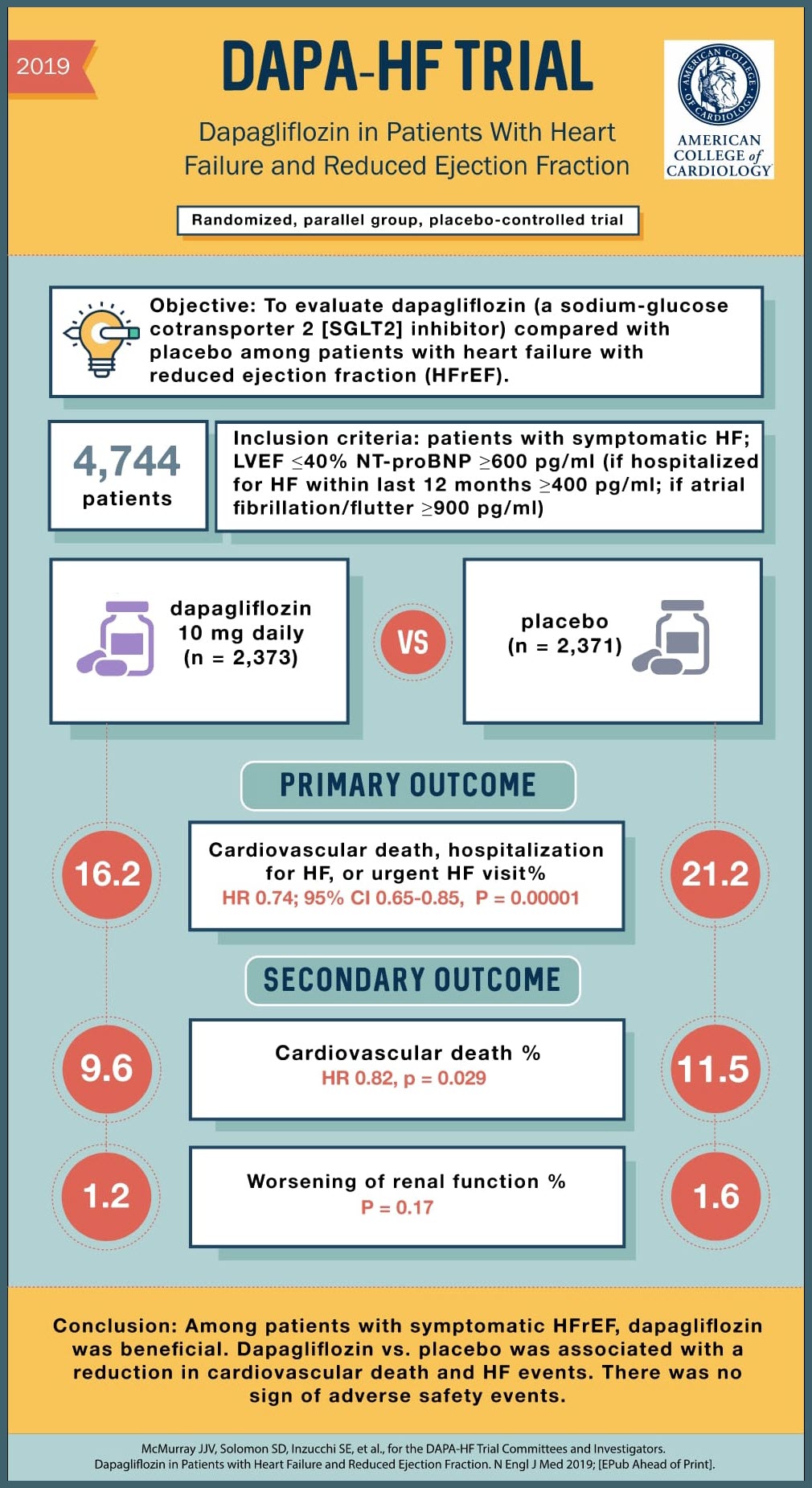
SOURCE: @Visualmedapp
SOURCE: @Visualmedapp
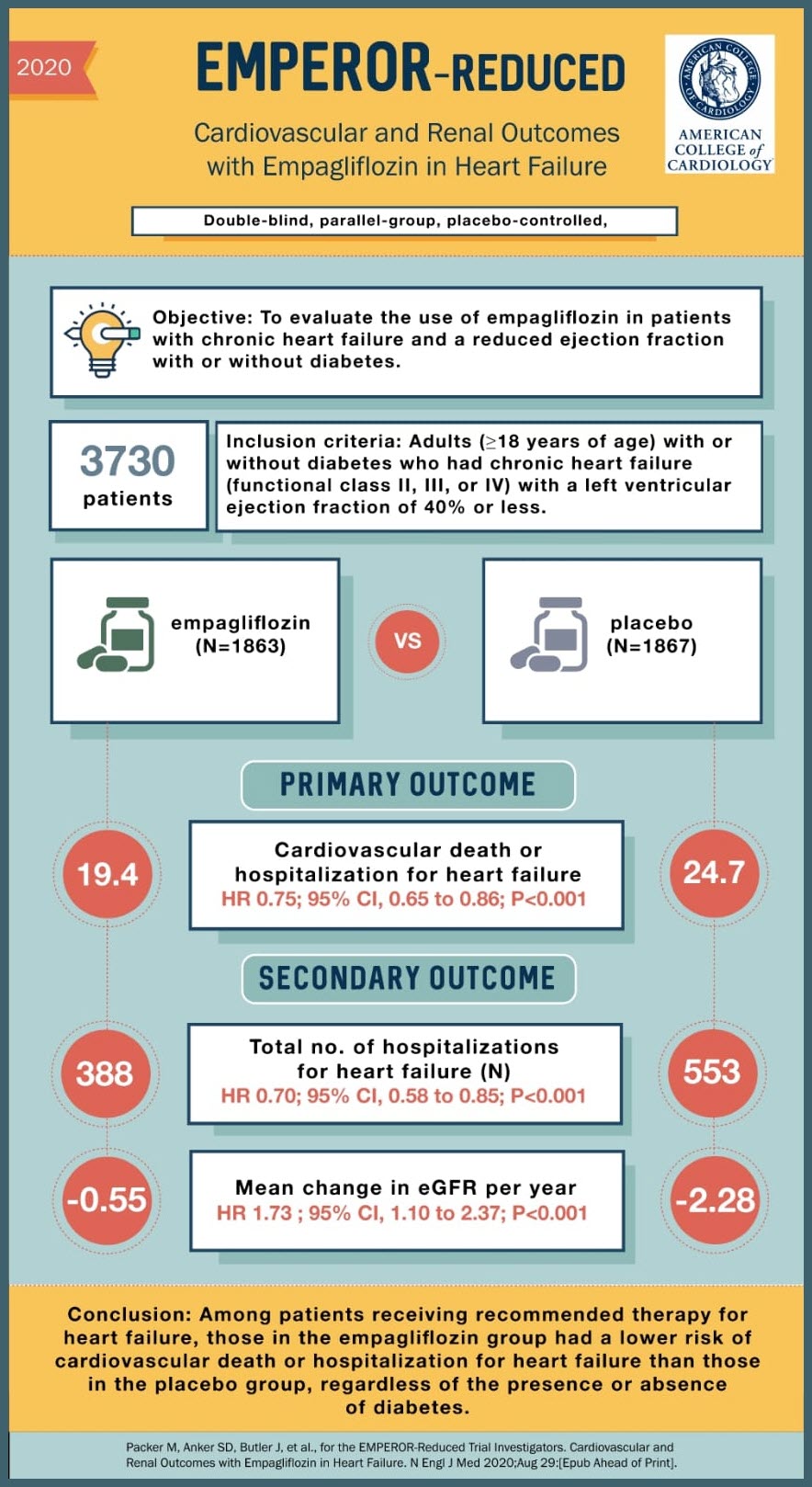
SOURCE: @Visualmedapp
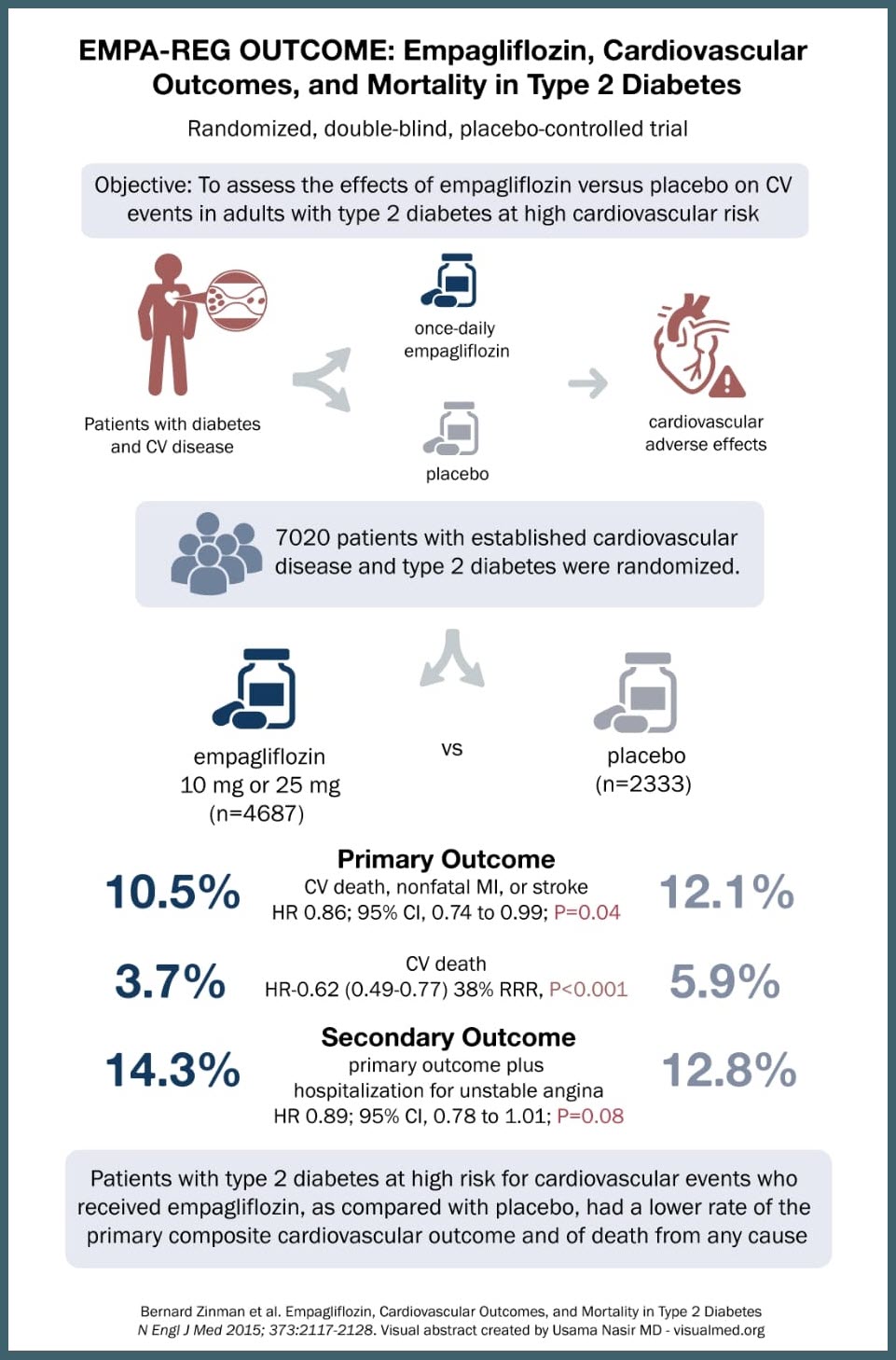
SOURCE: @Visualmedapp
SOURCE: @Visualmedapp
SOURCE: @Visualmedapp